Why Customer Journey Maps Matter
Every successful business prioritizes understanding its customers. But how do you truly see your product or service through the eyes of your audience? The answer lies in customer journey maps—a powerful tool that visualizes user interactions, touchpoints, and pain points to optimize their experience.
When businesses create journey maps, they gain valuable insights into user behavior, allowing them to:
- Identify friction points that lead to drop-offs.
- Optimize the customer experience for increased satisfaction.
- Improve engagement, retention, and conversion rates.
This guide will walk you through:
- What a customer journey map is and why it matters
- The key components of a journey map
- Step-by-step process for creating one
- Best practices to enhance the customer experience
By the end, you’ll understand how to craft a journey map that transforms customer interactions into lasting relationships.

What is a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of every touchpoint a user interacts with while engaging with your business. It provides a holistic view of the customer experience, from the first interaction to post-purchase loyalty.
Why is it Important?
- Enhances User Experience (UX): Helps brands tailor interactions for smoother customer engagement.
- Identifies Pain Points: Pinpoints where customers struggle or drop off in the journey.
- Boosts Conversions: A well-structured journey improves retention and sales.
- Aligns Teams: Ensures marketing, sales, and customer service teams understand the entire customer experience.
Example: Imagine an e-commerce company experiencing cart abandonment issues. A customer journey map can reveal where users drop off, helping the brand improve checkout flows and increase conversions.
Key Components of a Customer Journey Map
A well-structured journey map typically includes:
- Persona: The ideal customer profile engaging with your business.
- Touchpoints: Every interaction a customer has with your brand (e.g., website, social media, emails).
- Customer Goals: What the user aims to accomplish at each stage.
- Emotional Responses: The feelings customers experience throughout the journey.
- Pain Points: Frustrations or obstacles preventing conversion.
- Opportunities for Improvement: Areas where businesses can enhance the customer experience.
Pro Tip: Always map out customer emotions—understanding frustrations and expectations leads to actionable improvements.
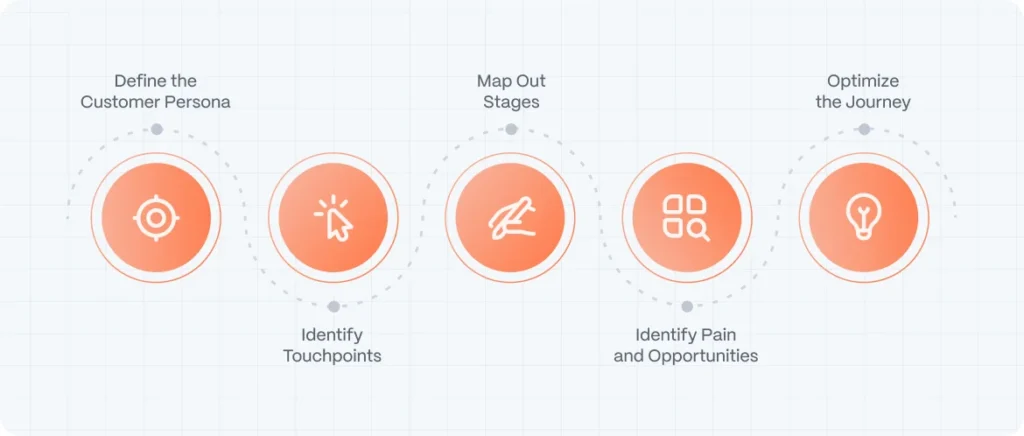
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Customer Journey Map
1. Define Your Customer Persona
- Identify who your customers are based on data (demographics, behaviors, pain points).
- Use analytics, surveys, and feedback to create a realistic persona.
Example: A SaaS startup may define a persona as “Sarah, a busy marketing manager looking for automation tools.”
2. Identify Customer Touchpoints
- List all potential ways a customer interacts with your brand (website, ads, social media, email, support, in-store).
- Group touchpoints into different stages of the funnel (Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, Retention).
Example: A DTC (direct-to-consumer) brand might have touchpoints including Instagram ads, landing pages, product pages, checkout, and post-purchase emails.
3. Map Out the Customer Journey Stages
Most customer journeys follow these five key stages:
| Stage | Customer Action | Business Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Discovers product via search, ad, referral | Optimize SEO, content marketing, social ads |
| Consideration | Researches brand, compares options | Use retargeting ads, reviews, case studies |
| Purchase | Adds product to cart, completes checkout | Streamline checkout UX, reduce friction |
| Retention | Uses product, receives support emails | Provide onboarding, engagement content |
| Advocacy | Leaves a review, refers friends | Implement loyalty programs, referral incentives |
Example: A B2B SaaS company might focus on longer consideration phases, requiring detailed case studies and free trials to convert leads.
4. Identify Pain Points and Opportunities
- Analyze drop-off points in analytics (e.g., high bounce rates, abandoned carts, low engagement).
- Collect customer feedback via surveys and heatmaps.
- Address friction areas (e.g., confusing navigation, unclear CTAs, long wait times).
Example: An e-commerce store might see high checkout abandonment due to unexpected shipping costs. A journey map helps identify fixes like free shipping incentives.
5. Optimize the Journey for Maximum Impact
- Automate marketing touchpoints (email sequences, chatbots, retargeting).
- Enhance personalization (dynamic content, personalized recommendations).
- Improve site UX (faster load times, clearer CTAs, intuitive navigation).
- Refine post-purchase engagement (follow-up emails, loyalty rewards).
Example: Spotify’s user journey includes personalized playlists to enhance retention and engagement.

Best Practices for Effective Customer Journey Mapping
- Use Data-Driven Insights – Rely on analytics, heatmaps, and surveys.
- Keep Maps Simple & Visual – Avoid cluttered, over-complicated diagrams.
- Update Maps Regularly – User behaviors change; keep maps up to date.
- Align Teams – Ensure marketing, sales, and UX teams collaborate.
- Prioritize Mobile Journeys – Mobile-first experiences are critical for engagement.
Example: Amazon optimizes every stage of the journey, ensuring smooth transactions, fast shipping, and personalized recommendations.