Accessibility in UX design is not just a legal obligation but a strategic advantage. By embracing inclusive design, startups can reach a broader audience, enhance user satisfaction, and tap into new markets. This article delves into the significance of accessibility and provides actionable insights for startups aiming to create inclusive user experiences.
Understanding Accessibility and Inclusive Design
Accessibility refers to designing products and services that are usable by people with varying abilities, ensuring equal access to information and functionality. According to the Interaction Design Foundation, accessibility is about optimizing the user experience for everyone, ensuring that content is accessible, inclusive, and user-friendly, regardless of ability.
Inclusive Design goes a step further by considering the full range of human diversity, including ability, language, culture, gender, and age. It involves creating solutions that cater to diverse needs, ensuring no user is left behind. The Interaction Design Foundation defines inclusive design as practices that take the spirit of accessible design further in user interfaces, ensuring clear and unambiguous messages that depict a diverse group of people.

The Business Case for Accessibility in UX Design
Expanding Market Reach
By implementing accessible design, startups can reach an estimated 1 billion people worldwide living with disabilities. This inclusivity not only fulfills ethical and legal standards but also opens up a significant market segment. The World Health Organization reports that over 1 billion people, about 15% of the world’s population, have some form of disability.
Enhancing User Experience
Accessible designs improve usability for all users, not just those with disabilities. Features like captions, voice controls, and adaptable interfaces enhance the overall user experience, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty. The Web Accessibility Initiative emphasizes that combining accessibility standards and usability processes with real people ensures that web design is technically and functionally usable by people with disabilities.
Legal Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Non-compliance with accessibility standards can lead to legal repercussions. In the U.S., the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) mandates accessible digital services, and failure to comply can result in lawsuits and financial penalties. The U.S. Department of Justice has stated that the ADA applies to websites and requires that they be accessible to people with disabilities.
Competitive Advantage
Startups that prioritize accessibility demonstrate social responsibility and innovation, setting themselves apart from competitors. This commitment can enhance brand reputation and attract a diverse customer base. The Web Accessibility Initiative notes that accessible design thinking provides varied and flexible ways for users to interact with websites and applications, options that are useful for people with and without disabilities.
Implementing Accessibility in UX Design: Best Practices
1. Adopt Inclusive Design Principles
Incorporate inclusive design principles from the outset to ensure accessibility is embedded in your product development process. The Interaction Design Foundation outlines 10 principles of accessibility that can guide designers in creating inclusive experiences. Here they are:
1. Blind gets 80% of accessibility issues
2. Image (alt-text) is classic
3. Hamburger menus are usually not accessible
4. Content placed “out of the way” won’t get found or seen
5. Accessibility testing with users can reveal huge gaps
6. Disabling zoom on mobile makes it inaccessible
7. Accessibility is easily learned
8. Accessibility does not mean ugly
9. Check mobile accessibility separately
10. Embrace the access atitude
Check the full vídeo here.
2. Conduct Accessibility Audits
Regularly evaluate your digital products to identify and address accessibility issues. Tools like WebAIM’s accessibility evaluation services can assist in this process.
3. Engage with Diverse User Groups
Involve individuals with diverse abilities in the design and testing phases to gain valuable insights and ensure your product meets their needs. Participatory design approaches can be particularly effective in this regard.
4. Stay Informed on Accessibility Standards
Keep abreast of the latest accessibility guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), to ensure compliance and best practices. The W3C’s Web Accessibility Initiative provides comprehensive resources on this topic.
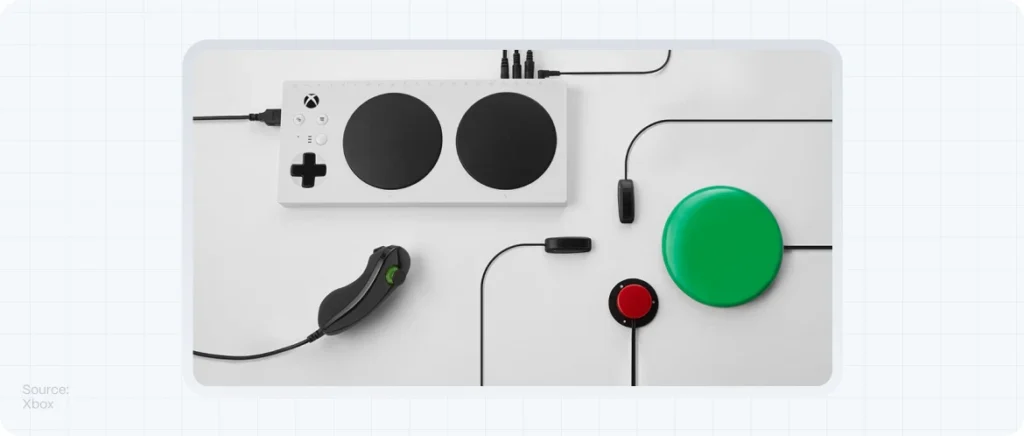

Case Study: Microsoft’s Commitment to Inclusive Design
Microsoft has been a pioneer in embracing inclusive design, creating products that cater to a diverse user base. Their approach involves recognizing exclusion, solving for one and extending to many, and learning from diversity. This strategy has led to the development of innovative features like the Xbox Adaptive Controller, designed for gamers with limited mobility. Microsoft’s inclusive design principles emphasize the importance of learning from people who represent different perspectives in the design process.
Accessibility in UX design
Accessibility in UX design is not merely a compliance requirement but a pathway to innovation, market expansion, and enhanced user satisfaction. By prioritizing inclusive design, startups can create products that resonate with a broader audience, fostering growth and success in an increasingly diverse digital world.
FAQ
What is the difference between accessibility and inclusive design?
Accessibility focuses on ensuring that products are usable by people with disabilities, meeting specific guidelines and standards. Inclusive design, on the other hand, considers the full range of human diversity, including ability, language, culture, gender, and age, aiming to create solutions that cater to as many people as possible.
What are some examples of companies successfully implementing inclusive design?
Microsoft is a leading example, with products like the Xbox Adaptive Controller, designed for gamers with limited mobility. Their inclusive design philosophy focuses on recognizing exclusion, solving for one user group, and extending solutions to many. This approach has led to innovative, user-friendly products that cater to a diverse audience.
How can startups test for accessibility?
Startups can:
-
Use automated tools like WAVE or AXE to identify technical accessibility issues.
-
Conduct user testing with individuals who have disabilities to gain real-world insights.
-
Perform manual audits to ensure compliance with WCAG guidelines.
-
How does accessibility align with legal requirements?
-
In the U.S., the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) mandates accessible digital services.
-
In the EU, the Web Accessibility Directive requires public sector websites and apps to meet WCAG standards.
Non-compliance can result in lawsuits, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
-